Table of Contents
What Is a Mileage Deduction?
A mileage deduction allows individuals and businesses to reduce their taxable income by accounting for the business use of a personal vehicle. Claiming mileage on taxes is possible when a vehicle is used for business, medical, charitable, or, in certain cases, moving purposes.
Deduction Methods
There are two primary methods to calculate deductible vehicle expenses:
1. Standard Mileage Rate
This method involves multiplying the total business miles driven by the IRS-established standard mileage rate. The rate is updated annually and encompasses expenses such as fuel, maintenance, depreciation, and insurance.
Eligibility Criteria:
The vehicle must be owned or leased by the taxpayer.
The standard mileage rate must be chosen in the first year the vehicle is used for business.
The taxpayer must not have claimed depreciation deductions other than straight-line depreciation.
The vehicle must not be part of a fleet of five or more vehicles used simultaneously.
2. Actual Expense Method
This approach requires detailed tracking of all actual vehicle-related expenses, including:
Fuel
Maintenance and repairs
Insurance
Registration fees
Depreciation or lease payments
The deductible amount is calculated based on the percentage of total vehicle use that is for business purposes.
Recordkeeping Requirements
To substantiate mileage deductions, the IRS mandates maintaining accurate and timely records. Essential information includes:
Date of each trip
Purpose of the trip
Starting point and destination
Beginning and ending odometer readings
Total miles driven per trip
Records should be kept contemporaneously, meaning they should be recorded at or near the time of the trip. If the trips are very obviously forged after the fact, the IRS can issue a penalty and revoke your deduction.
Non-Deductible Mileage
It’s important to note that commuting miles—the distance traveled from home to the regular place of work—are not deductible. Only mileage incurred for business-related activities beyond the regular commute qualifies for deduction.
Additional Considerations
Parking Fees and Tolls: These are deductible separately from the standard mileage rate, provided they are business-related.
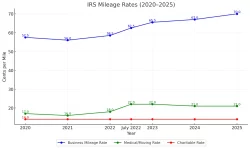
Charitable Mileage and Medical Mileage: Different rates apply for mileage driven for charitable or medical purposes. These rates are also set by the IRS and are subject to annual updates.
Note that there are many deduction opportunities available for self-employed people. Look for them on official platforms or a deduction finder tool covered in our Everlance review.
For the most current mileage rates and detailed guidelines, refer to the IRS’s official publications or consult a tax professional.
FAQ
What is a mileage deduction?
A mileage deduction allows taxpayers to claim the cost of using their personal vehicle for business purposes as a tax-deductible expense, reducing taxable income.
How do I calculate my mileage deduction?
You can calculate your deduction using either the standard mileage rate set by the IRS or by recording actual vehicle expenses and allocating them proportionally to business use. Apps like Triplog , the Driversnote mileage app, and MileIQ automatically track your miles and calculate your deductions.
Am I eligible for mileage deduction?
You’re eligible for a mileage deduction if you use your personal vehicle for business (for example, if you are a real estate agent), medical, moving (for active-duty military), or charitable purposes.
How does MileageWise simplify mileage deduction tracking?
MileageWise provides automatic mileage tracking, accurate documentation, and simple mileage logs, making it easy to claim your mileage deduction.